You're a manager on a mission, with an ambitious vision to elevate your company's online store.
In your mind, the goals are crystal clear — but potential roadblocks and growing workloads prevent you from seeing initiatives through.
To ensure your project’s success, you need to translate those conceptual goals into a clear, organized plan. Using a business requirements document (BRD) to put your plan into words will help you launch your project and keep your team on track. Learn how this handy tool can move your initiatives in the right direction.
What’s a business requirements document, and why is it important?
A BRD is a detailed record outlining everything a team requires to efficiently execute initiatives, from ideation to delivery.
When you develop a thorough BRD framework, you'll evaluate a new initiative’s requirements to allocate resources effectively and create risk mitigation plans. These documents also make it easy to see how individual projects support and align with your team’s long-term vision.
Business requirements versus functional requirements
Business requirements specify an initiative’s purpose and the resources and general strategy you’ll use to complete it. And functional requirements outline specific, actionable tasks based on business requirements and resources. So, a BRD informs a project’s functional requirements.
Here are a few more ways these essentials differ.
Business requirements
Essential elements of business requirements include:
Attention to stakeholders — business requirements center around satisfying the expectations and preferences of various stakeholders, including investors, employees, and customers.
Non-technical terminology — using simple language, business requirements ensure everyone involved understands the project's purpose, regardless of technical expertise.
A holistic long-term approach — business requirements focus on a company’s overarching objectives instead of outlining specific technical details or precise implementation strategies.
An example of a business requirement for an SaaS company may be to “increase app downloads by 15% over the next quarter.”
Functional requirements
The more detailed functional requirements include:
Attention to users — functional requirements focus on a product’s final user experience, detailing how end-users interact with your product or service (such as a website, app, or system).
Technical terminology — defining functional requirements with highly technical language helps knowledgeable professionals like developers understand your project’s specific features and execution methods.
Project-basis approach — functional requirements provide team members with clear directions and actionable steps to meet business requirements.
An example of a functional requirement for a SaaS company may be to “launch an email marketing campaign with calls-to-action (CTAs) encouraging users to download the app.”
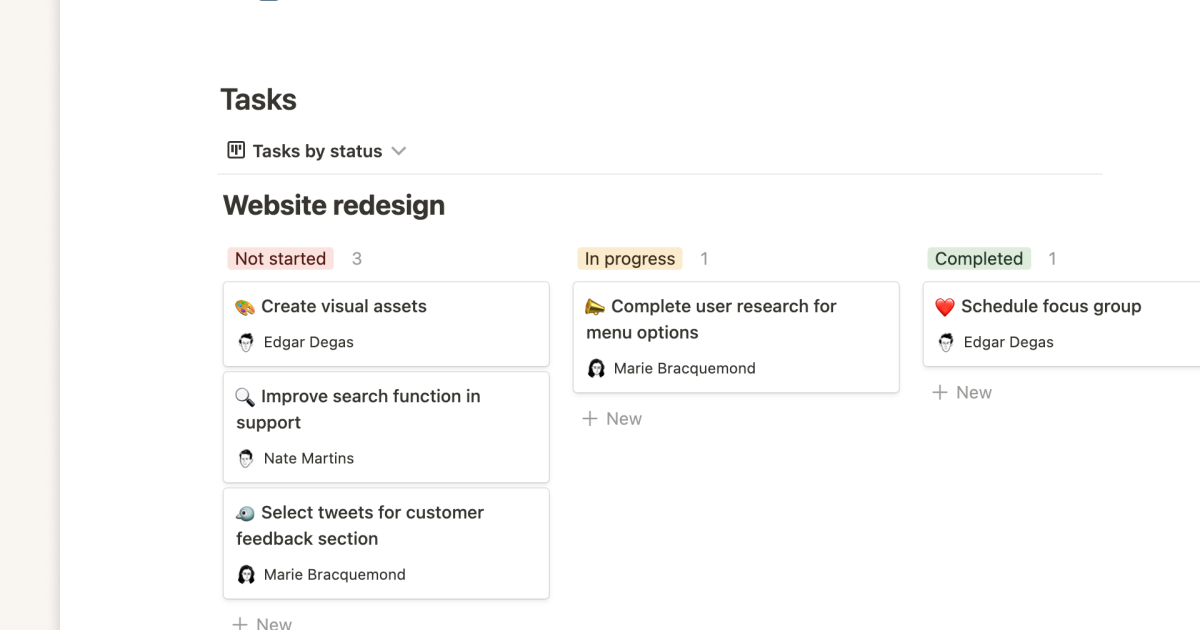
Key elements of a business requirements document
BRD content overlaps with other project-related documentation, like contracts and business proposals. Here are a few overlapping and unique elements these documents typically contain.
Executive summary
An executive summary is a brief overview of your BRD. Like an elevator pitch, this summary concisely defines your project’s objectives, key deliverables, and major requirements. Stakeholders can then reference this description to comprehend the project’s purpose and resources at a glance.
Imagine you own an online clothing shop and want to boost sales by 25% during the next fiscal year. In your BRD’s executive summary, you’d highlight the general goal of increasing online sales through the website and app.
Objectives
Clear objectives provide direction, giving your project structure and meaning. In this section, you'll describe specific, measurable, and realistic goals that align with your company's long-term vision.
In the context of an online shop, your project's objectives section can include increasing website traffic, developing a secure payment gateway, and offering multi-language support to appeal to a broader audience.
Project statement
The project statement comprehensively describes your project’s context and advocates for its necessity. It also acknowledges any potential opportunities to seize or challenges to work through. To receive key stakeholder buy-in, include statistics and research to support your claims.
Your sales growth project statement might explain how you can expand your online market by offering competitive prices and improving customer satisfaction.
Project scope
In this section, you'll determine the projection’s limitations. A well-defined scope sets boundaries to prevent scope creep, ensuring the project doesn't stray from the initial plan and overwhelm team members with additional work.
Let's say you want to create a new web page for your company’s summer sale. The scope would include various features, like a product catalog, shopping cart functionality, and multiple payment methods. And any added elements that cross your scope’s boundaries would lead to scope creep.
Requirements
Here’s where business requirements meet functional requirements. In this part of your BRD, you'll flesh out broader objectives with precise technical details, providing a reference for the design, development, and testing phases.
Functional requirements for a web page would outline the steps for developing features like a search bar, product filters, and PayPal integration. Teammates can refer to these guidelines as they work.
Key stakeholders
This section addresses entities interested in your project and their expectations for its success. Identifying key stakeholders ensures all parties remain responsible and accountable for their roles in the initiative, and that you consider their interests and opinions before making decisions.
Key stakeholders can include internal and external individuals and groups, such as managers, design teams, and clients.
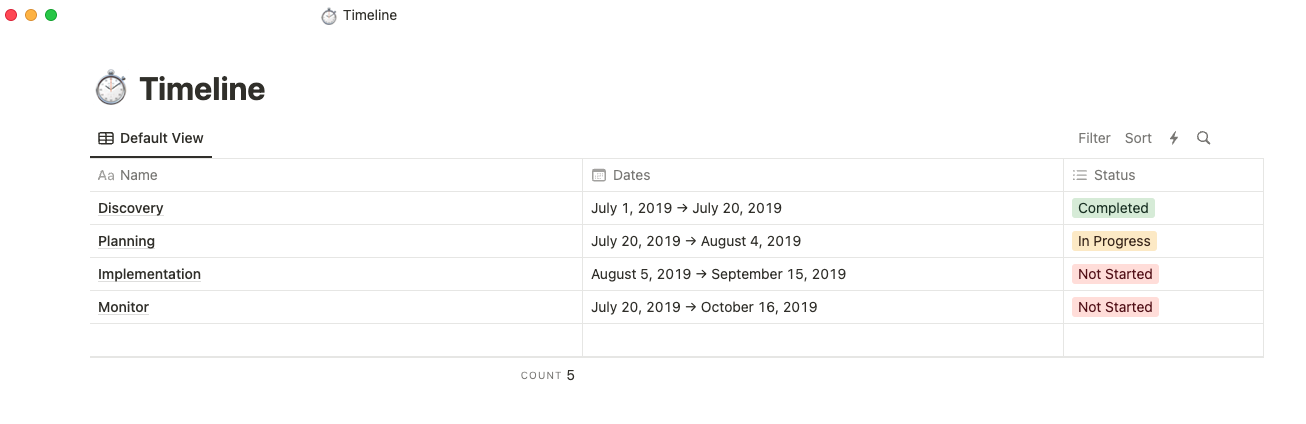
Deadlines
This is where you'll establish a project schedule with benchmarks, phases, and delivery dates. Setting deadlines ensures all stakeholders understand the project's timeline and can plan for resource allocation and progress tracking. It also helps manage expectations throughout the process.
Your sales site might use the following timeline:
Month one: Complete web page design
Month two: Start developmentMonth four: Launch website
Some managers craft their timelines using project management templates which helps teams monitor progress, receive updates, and keep track of deadlines.
Cost-benefit analysis
A cost-benefit analysis helps gauge your return on investment (ROI) by outlining and comparing projected costs to expected results. This section allows you to determine the project's economic viability and whether it's worth pursuing.
A practical cost-benefit analysis for your clothing site would estimate website development, server hosting, and maintenance expenses. The output and income will justify the costs if you see a positive ROI.
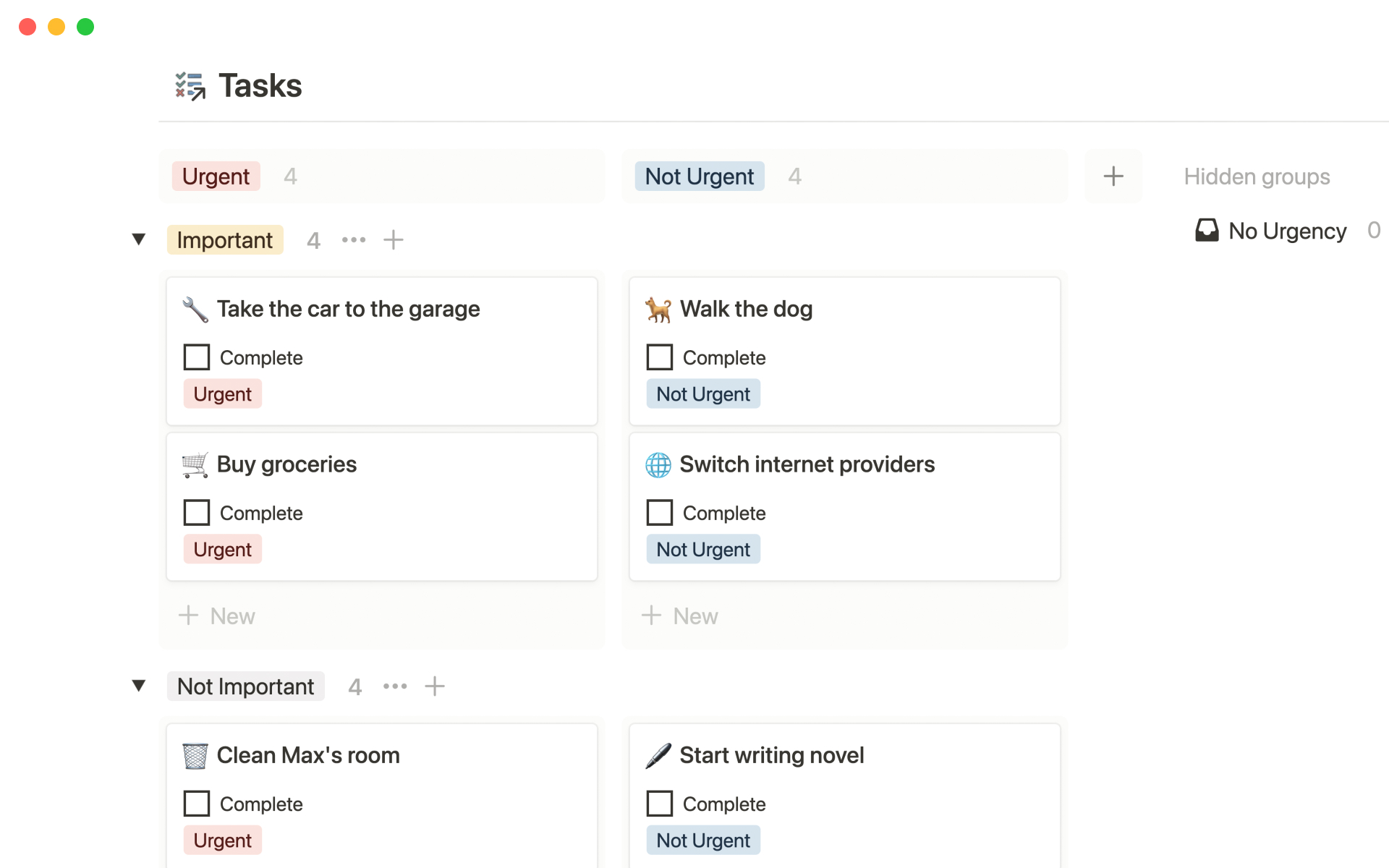
How to write a business requirements document: 5 tips
Here are five best practices to guarantee a well-drafted BRD:
Refer to past projects — reviewing former projects reveals valuable insights. You can learn from previous mistakes and leverage proven methods to improve your project's chance of success.
Set the right goals — ensure your project aligns with your employer's overarching objectives and clarify expectations for all key stakeholders. This establishes common goals for all parties and a clear direction for the project.
Encourage collaboration — involve project managers, team members, and end-users from the start, as their feedback helps you address the right pain points. Maintain this collaborative communication style throughout the project to streamline workflows and improve efficiency.
Avoid jargon — apart from your functional requirements section, avoid using industry-specific terms only technical experts understand. Write in plain language to ensure everyone involved comprehends the requirements.
Use a template — choose or create a BRD template that aligns with your company's needs. A consistent, standardized format clarifies current and future projects and saves time. And a well-crafted template ensures you cover all the necessary sections without overlooking key elements.
An effective example of a business requirements document
Here’s an example of a well-designed BRD for the hypothetical clothing website to help you structure your own.
Project title: Enhancing the user experience for [company name] to increase online sales.
Prepared by: [your name]
Date: September 15, 2023
1. Executive summary
Our company, [company name], is looking to develop a project management system to monitor and improve multiple business requirements, including online sales, employee communication, and brand awareness.
The tentative project timeline will run from the beginning of the fourth quarter of 2023 (October 1st) until the end of the first quarter of 2024 (March 31st). We aim to achieve these business requirements with the involvement of key stakeholders, including a project manager, department leads, and team members.
This business requirements document outlines this project management system, the objectives, project statement, scope, requirements, key stakeholders, deadlines, and cost-benefit analysis.
2. Objectives
Expand the product catalog by 15%
Implement a secure payment gateway for online transactions, including PayPal and Stripe integration
Improve user experience through intuitive navigation and responsive design
Increase website traffic by 25%
3. Project statement
This project aims to meet the changing demands of our target audience and existing customer base. By improving the website and app's user experience and integrating secure payment gateways, we look to capture a larger share of the growing online apparel market, strengthen customer loyalty, and boost sales.
The company requires a project management system to guide website developers, designers, marketing teams, and other stakeholders. Outsourcing human capital will cost an average of $28,750 per quarter, and implementing this system will allow the company to save money and promote in-house skill development.
4. Project scope
Add a product search and filtering system to sort catalogs
Develop a responsive design that adapts to multiple screen sizes and devices
Integrate encrypted payment processing with reputable third-party portals, including PayPal and Stripe
Link a reliable content management system (CMS) for product updates
Redesign the website and app interfaces to improve visual appeal and usability
5. Requirements
Content management system for product updates
Customer profile creation and management
Efficient product review and rating system (comments and 5-star ratings)
Order tracking and history (over three, six, and 12 months)
Product search with relevant filters (category, brand, price, color, size)
Responsive website design for multiple devices and screens
Secure payment integration (PayPal and Stripe)
Shopping cart functionality
6. Deadlines
Design phase — Month one
Development phase — Months 2–3
User testing phase — Month four
Feedback and revisions phase — Month five
Website and app launch — Month six
7. Cost-benefit analysis
Estimated project expenditure — approximately $120,000
Projected increase in website traffic — 23.5%
Projected increase in sales — 18%
Return on investment — 123%
Complete every requirement with Notion
Whether you work for a budding startup or an established enterprise, your project's success depends on fruitful collaboration, efficient operations, and high-quality client deliverables.
To achieve this, you need more than a business requirements document template — and Notion can equip you with the best tools.
With hundreds of templates, Notion streamlines workflows and makes executing effective business plans easy. Search our template gallery for something that perfectly suits your team’s needs.