Wilson's disease is an autosomal recessive disorder characterised by excessive copper deposition in the tissues. Metabolic abnormalities include increased copper absorption from the small intestine and decreased hepatic copper excretion. Wilson's disease is caused by a defect in the ATP7B gene located on chromosome 13.
The onset of symptoms is usually between 10 - 25 years. Children usually present with liver disease whereas the first sign of disease in young adults is often neurological disease
Features result from excessive copper deposition in the tissues, especially the brain, liver and cornea:
- liver: hepatitis, cirrhosis
- neurological:
- basal ganglia degeneration: in the brain, most copper is deposited in the basal ganglia, particularly in the putamen and globus pallidus
- speech, behavioural and psychiatric problems are often the first manifestations
- also: asterixis, chorea, dementia, parkinsonism
- Kayser-Fleischer rings
- green-brown rings in the periphery of the iris
- due to copper accumulation in Descemet membrane
- present in around 50% of patients with isolated hepatic Wilson's disease and 90% who have neurological involvement
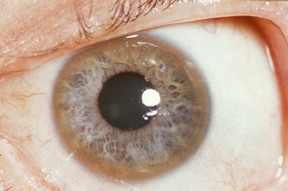
Example of Kayser-Fleischer ring
- renal tubular acidosis (esp. Fanconi syndrome)
- haemolysis
- blue nails
Investigations
- slit lamp examination for Kayser-Fleischer rings
- reduced serum caeruloplasmin
- reduced total serum copper (counter-intuitive, but 95% of plasma copper is carried by ceruloplasmin)
- free (non-ceruloplasmin-bound) serum copper is increased
- increased 24hr urinary copper excretion
- the diagnosis is confirmed by genetic analysis of the ATP7B gene
Management
- penicillamine (chelates copper) has been the traditional first-line treatment
- trientine hydrochloride is an alternative chelating agent which may become first-line treatment in the future
- tetrathiomolybdate is a newer agent that is currently under investigation

