Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition which results in the loss of melanocytes and consequent depigmentation of the skin. It is thought to affect around 1% of the population and symptoms typically develop by the age of 20-30 years.
Associated conditions
- type 1 diabetes mellitus
- Addison's disease
- autoimmune thyroid disorders
- pernicious anaemia
- alopecia areata
Features
- well-demarcated patches of depigmented skin
- the peripheries tend to be most affected
- trauma may precipitate new lesions (Koebner phenomenon)
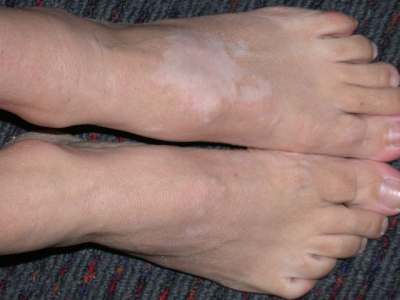
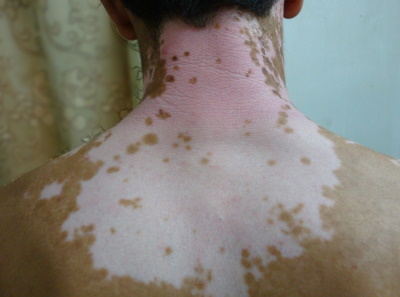
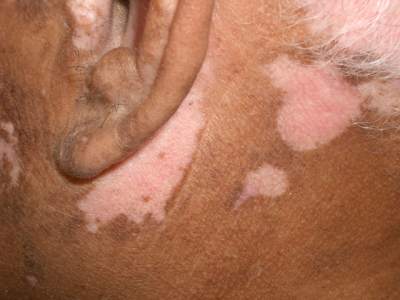
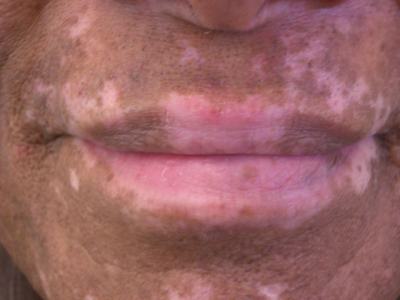
Management
- sunblock for affected areas of skin
- camouflage make-up
- topical corticosteroids may reverse the changes if applied early
- there may also be a role for topical tacrolimus and phototherapy, although caution needs to be exercised with light-skinned patients




