Rosacea
Rosacea (sometimes referred to as acne rosacea) is a chronic skin disease of unknown aetiology.
Features
- typically affects nose, cheeks and forehead
- flushing is often first symptom
- telangiectasia are common
- later develops into persistent erythema with papules and pustules
- rhinophyma
- ocular involvement: blepharitis
- sunlight may exacerbate symptoms

Rosacea - showing papules, pustules and erythema. Image used on license from DermNet NZ
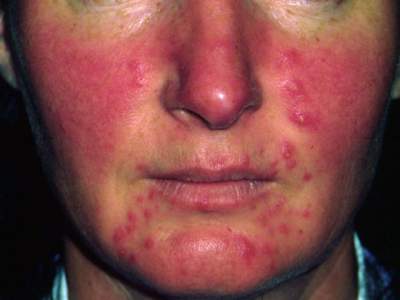

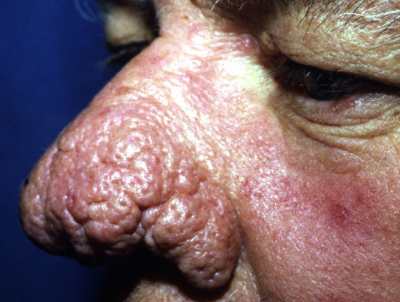

Rosacea over the cheeks and nose
Management
- simple measures
- recommend daily application of a high-factor sunscreen
- camouflage creams may help conceal redness
- predominant erythema/flushing
- topical brimonidine gel may be considered for patients with predominant flushing but limited telangiectasia
- brimonidine is a topical alpha-adrenergic agonist
- this can be used on an 'as required basis' to temporarily reduce redness
- it typically reduces redness within 30 minutes, reaching peak action at 3-6 hours, after which the redness returns to the baseline
- mild-to-moderate papules and/or pustules
- topical ivermectin is first-line
- alternatives include: topical metronidazole or topical azelaic acid





