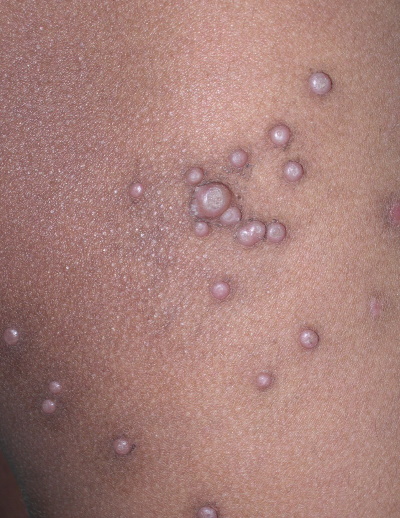
Molluscum contagiosum is a common skin infection caused by molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV), a member of the Poxviridae family. Transmission occurs directly by close personal contact, or indirectly via fomites (contaminated surfaces) such as shared towels and flannels. The majority of cases occur in children (often in children with atopic eczema), with the maximum incidence in preschool children aged 1-4 years.
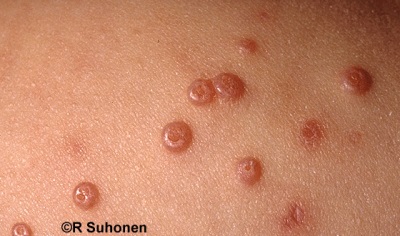
Typically, molluscum contagiosum presents with characteristic pinkish or pearly white papules with a central umbilication, which are up to 5 mm in diameter. Lesions appear in clusters in areas anywhere on the body (except the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet). In children, lesions are commonly seen on the trunk and in flexures, but anogenital lesions may also occur. In adults, sexual contact may lead to lesions developing on the genitalia, pubis, thighs, and lower abdomen. Rarely, lesions can occur on the oral mucosa and on the eyelids.

Molluscum contagiosum in a child. The image demonstrates the typical pearly papules with umbilicated centres

Molluscum contagiosum. Image used on license from DermNet NZ
Self-care advice:
Treatment is not usually recommended. If lesions are troublesome or considered unsightly, use simple trauma or cryotherapy, depending on the parents' wishes and the child's age:
Referral may be necessary in some circumstances: