| Type | Injury pattern |
|---|---|
| Complete fracture | Both sides of the cortex are breached |
| Toddlers fracture | Oblique tibial fracture in infants |
| Plastic deformity | Stress on bone resulting in deformity without cortical disruption |
| Greenstick fracture | Unilateral cortical breach only |
| Buckle ('torus') fracture | Incomplete cortical disruption resulting in periosteal haematoma only |
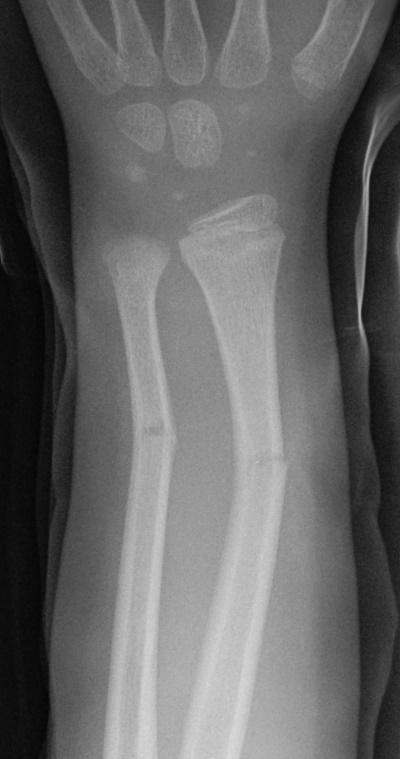
is the correct answer. It is strongly recommended to research the above types of fractures for a better understanding of their x-ray presentation. A green-stick fracture involves an incomplete fracture usually at the shaft of a long bone (as seen here in the radius and ulna). It is caused by a bending-type mechanism of injury. As with all fractures in children, it is important to consider safeguarding issues, especially with mechanisms of injury as such.
is incorrect. This type of fracture is usually caused by a compression force. This would create a 'buckle' as if the bone was 'shortened'. This is can be very commonly missed due to the subtle deformity it causes. It usually causes buckling of one side but if the compression is strong enough it can cause more severe deformity.
is incorrect. As the name suggests this type of fracture would involve a 'transverse', almost like a horizontal line cutting through the shaft, and 'complete', meaning that the fracture line went through the shaft from one side to the other. This is commonly seen in direct-impact trauma (e.g. playing sports in children).
is incorrect. This is a common fracture in the children population and it involves the tibia. It is a spiral fracture of the shaft of the tibia with an intact fibula. This is unlikely in this case the forearm is being shown on the x-ray. This type of fracture is notorious for raising safeguarding issues due to the nature of its mechanism of injury, meaning that it can potentially be caused by forceful twisting of the leg by someone. However, this is not always the case.

Greenstick fracture - e Image used on license from Radiopaedia
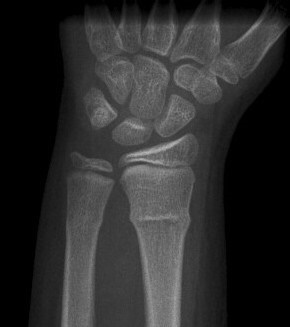
Buckle (torus) fracture - e Image used on license from Radiopaedia
is incorrect. This is a type of fracture that involves the epiphyseal plate in children. This child still has its radius and ulna epiphyseal plates growing so it would be a candidate for it. However, the abnormality is found in the shaft of the bones and not in the epiphyseal plates. There are classically 5 types that can be remembered with the mnemonic SALTER with each letter corresponding to a type: