
Sue Hyun Park, August 23.
<aside> 🔗 We have reposted this blog on our Medium publication. Read this on Medium.
</aside>
Pose is a typical non-verbal expression of humans. As poses make up gestures and actions, the human pose information is important for human behavior understanding, human computer interaction, and AR/VR. Besides the body pose, poses of specific body parts like the hand are also important because hand motions can communicate intention or feeling that body-driven large motions cannot, and hands are widely used for interactions with objects. Human pose estimation is a computer vision task of detecting and analyzing human posture, technically by localizing semantic keypoints (i.e., joints) of human body parts in 3D space.
As the task has been studied for well over decades, you can meet many applications in real life that have pose estimation technologies integrated — motion captures in movies, fitness assistants, games, surveillance cameras, and so on.

AI-based fitness apps (Source: Solution Analysts)
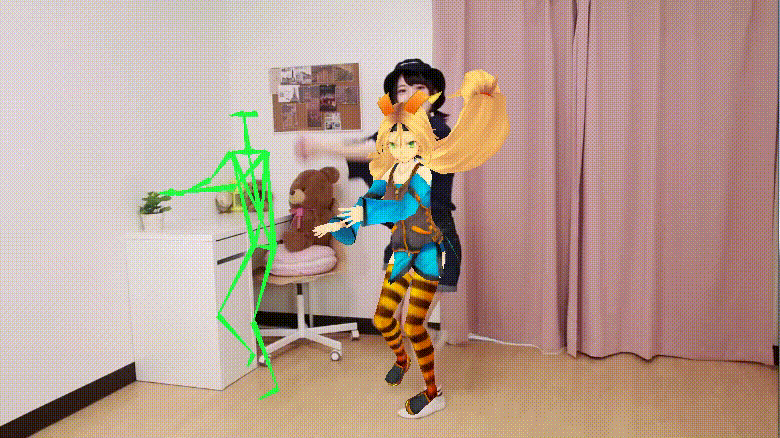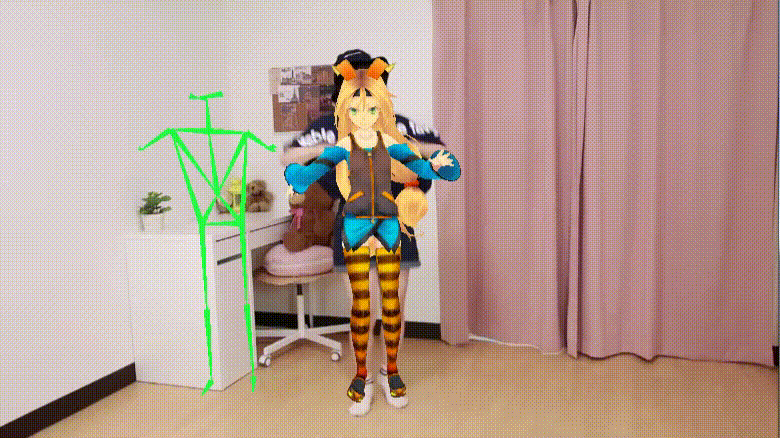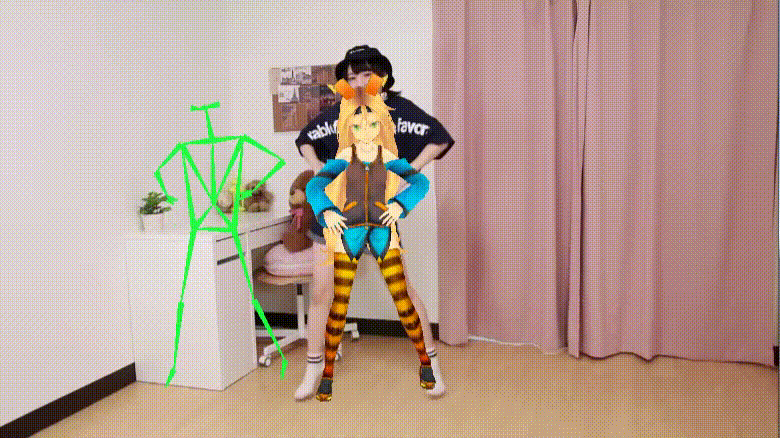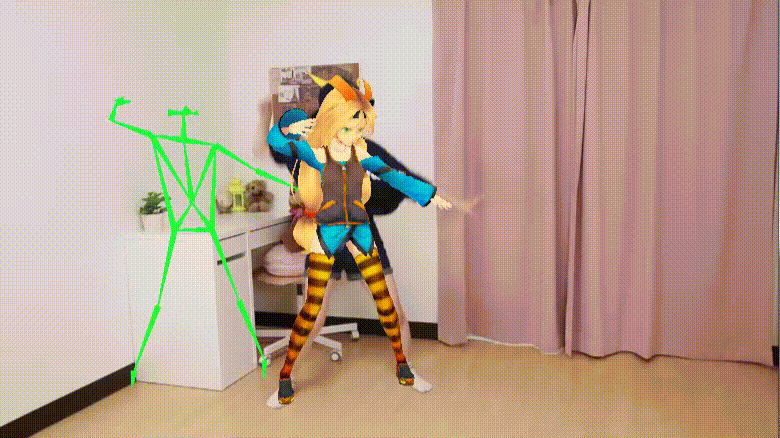
Real-time moving avatar (Source: UnityList)
A variety of services capture the volume and shape too.

Virtual try-on and AR fitting (Source: FXMirror)

Interactive "blobs" with the Leap Motion Controller on the new portrait Looking Glass. (Source: Ultraleap)

AR Emoji (Source: Samsung)
There are several input sources to estimate 3D human pose and shape from, whether it be synthesized or real, a depth map or an RGB image, and/or from multiple views or just a single view. for the 3D rotation and mesh data can lead to more expressive figures of the human hand. The 3D human poses and shape estimation task expands from the pose-only case, but we work on slightly different aspects.

Comparison of hand images from datasets of Mueller et al., RHP, Simon et al., and FreiHAND. An RGBD image is a combination of an RGB image and its corresponding depth image.
A 3D human pose and shape estimation model can be more adaptable to everyday cases when it is trained with a real single RGB image. After all, the cameras we normally use are RGB-based and we expect a single input for a single output. The shortcoming is that a flat 2D image has depth and scale ambiguity, making the human articulation process even more complicated.
In the following two blog posts, we introduce our novel methods to compose 3D human pose and shape information from a single RGB image despite the 2D-to-3D ambiguity.
In part 1, we describe our work on 3D human pose estimation. We focus on localizing joints of human bodies and hands in the 3D space in order to lay the cornerstone for vital 2D-to-3D conversion techniques. These include accurately measuring a subject's relative distance from the camera for multi-person scenarios and depicting the complex sequence of interacting hands.
In part 2, we describe how our work extends to estimating the human mesh, a widely used data format for 3D human shape representation. In the end, we simultaneously localize joints and mesh vertices of all human parts, including body, hands, and face, for more rich and comprehensive 3D figures. Reaching this state, we discuss how advanced 3D human pose and shape estimation methods can be applied in industries to lead the advent of new communication technologies.
This blog, part 1, is dedicated to 3D human pose estimation techniques that focus on delivering:

3D multi-person pose estimation

3D human interacting-hand pose estimation