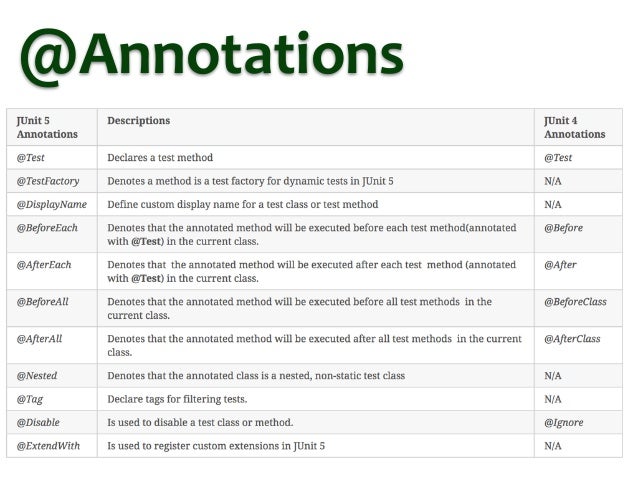

本图来自 Ismael 在 Slideshare 分享的 JUnit 5 vs JUnit 4
接下来来我们来一个个注解详细介绍。
如 JUnit5 VS JUnit4 图中所示,@BeforeAll是替换 JUnit4 的@BeforeClass。它用于表示在当前测试类中的所有测试之前应该执行注解的方法。
@BeforeAll
public void init(){
System.out.println("Before All init() method called");
}
@BeforeAll注解方法必须是静态方法,否则会抛出运行时错误。
org.junit.platform.commons.JUnitException: @BeforeAll method 'public void com.github.tonydeng.junit5.examples.JUnit5AnnotationsExample.init()' must be static.
at org.junit.jupiter.engine.descriptor.LifecycleMethodUtils.assertStatic(LifecycleMethodUtils.java:66)
at org.junit.jupiter.engine.descriptor.LifecycleMethodUtils.lambda$findBeforeAllMethods$0(LifecycleMethodUtils.java:42)
at java.util.ArrayList.forEach(ArrayList.java:1249)
at java.util.Collections$UnmodifiableCollection.forEach(Collections.java:1080)
at org.junit.jupiter.engine.descriptor.LifecycleMethodUtils.findBeforeAllMethods(LifecycleMethodUtils.java:42)
我们来举个例子。我使用了一个Calculator类并添加了一个add方法。我将使用@RepeatedTest注解测试它 5 次。此注解将导致add测试运行 5 次。但@BeforeAll注解方法只能调用一次。
package com.github.tonydeng.junit5.examples;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.RepeatedTest;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.TestInfo;
import org.junit.platform.runner.JUnitPlatform;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
@RunWith(JUnitPlatform.class)
public class JUnit5AnnotationsExample {
@Test
@DisplayName("Add operation test")
@RepeatedTest(5)
void addNumber(TestInfo testInfo) {
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
Assertions.assertEquals(2, calculator.add(1, 1), "1 + 1 should equal 2");
}
@BeforeAll
public static void init(){
System.out.println("Before All init() method called");
}
}
计算器类是:
package com.github.tonydeng.junit5.examples;
public class Calculator
{
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
}
现在执行测试,您将在控制台输出下方看到:
Before All init() method called